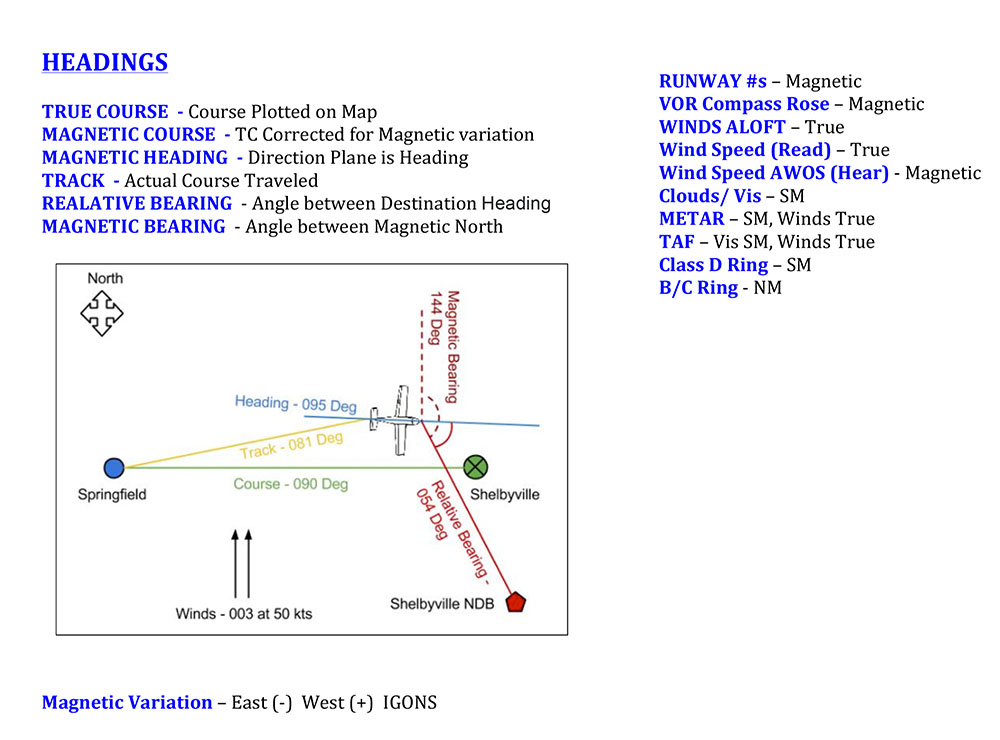
Magnetic Course Vs Magnetic Heading
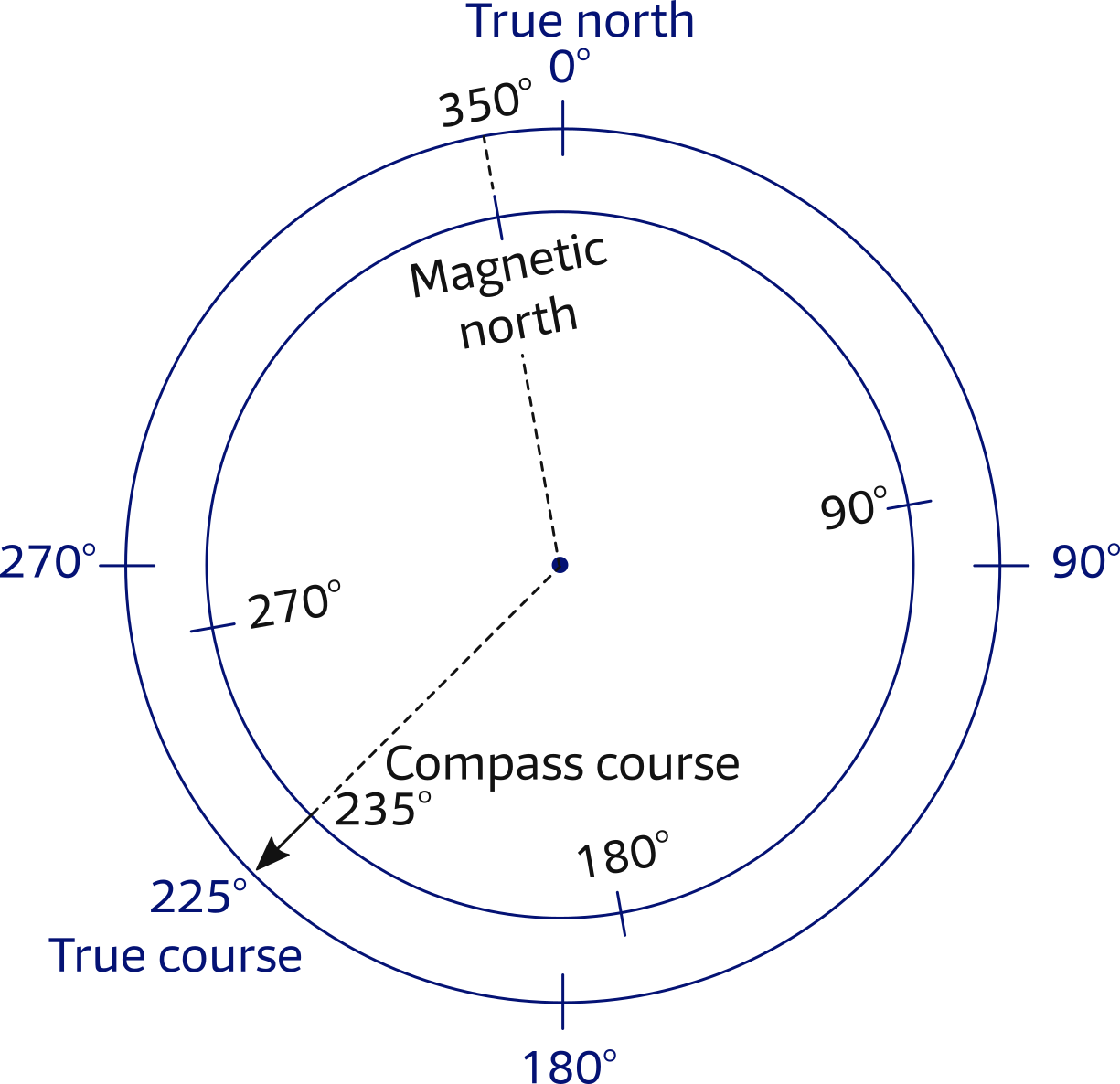
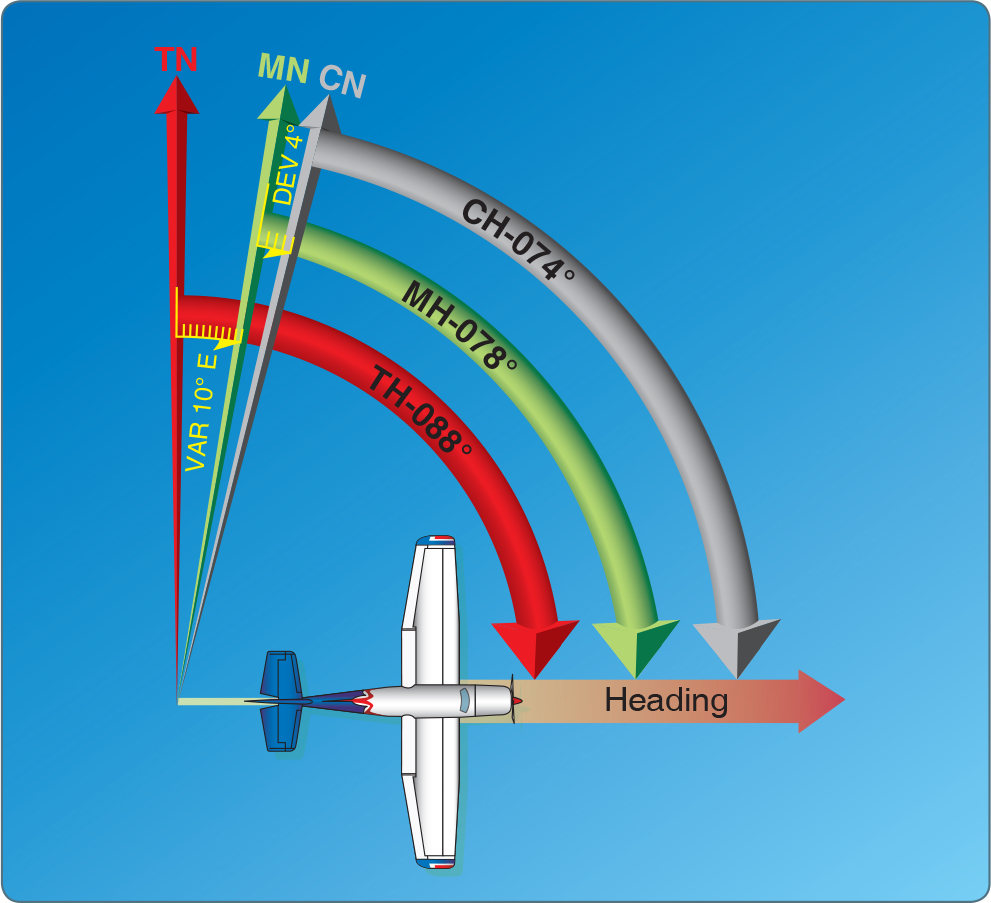
Magnetic Course Vs Magnetic Heading - Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). See answers from pilots and experts on askacfi.com, a forum for flight training questions. Bearing is the angle between any two. In this article we discuss navigation concepts and look at the differences between course and heading. Intuitively, ground track should be a true course as it is (presumably). The reference is the north of the earth’s magnetic. While they are related, they refer to. Magnetic course (mc) is the direction over the. There are a lot of different terms that we use when we plan flights: Magnetic heading is where the airplane is pointed. There are a lot of different terms that we use when we plan flights: Learn the differences and roles of true course, true heading, and magnetic heading in aviation navigation. Magnetic course (mc) is the direction over the. Your magnetic heading, corrected via use of the. Bearing is the angle between any two. While they are related, they refer to. Find out how to calculate them and why they matter for pilots. Is the ground track (trk in garmin) a magnetic or a true course or does it depend on a specific gps unit? Magnetic course is the airplane’s course across the ground, relative to magnetic north. The reference is the north of the earth’s magnetic. Find out how to calculate them and why they matter for pilots. Learn the differences and roles of true course, true heading, and magnetic heading in aviation navigation. See answers from pilots and experts on askacfi.com, a forum for flight training questions. Magnetic course is the airplane’s course across the ground, relative to magnetic north. Your magnetic heading, corrected via. The difference between magnetic course (mc) and magnetic heading (mh) lies in their references to direction in navigation. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). We will call course the trajectory to follow, it is the planned. The difference between true north and magnetic north is known as variation. Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. We will call course the trajectory to follow, it is the planned or desired. Intuitively, ground track should be a true course as it is (presumably). The. Find out how to calculate them and why they matter for pilots. Learn the definitions and differences of these three terms related to aircraft orientation and trajectory. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). There are a. The difference between true north and magnetic north is known as variation. There are a lot of different terms that we use when we plan flights: Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). Is the ground track. In this article we discuss navigation concepts and look at the differences between course and heading. The reference is the true north, the closest point to the axis of rotation of the planet; There are a lot of different terms that we use when we plan flights: Find out how to calculate them and why they matter for pilots. Magnetic. The difference between true north and magnetic north is known as variation. Learn the differences and roles of true course, true heading, and magnetic heading in aviation navigation. While they are related, they refer to. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses. Is the ground track (trk in garmin) a magnetic or a true course or does it depend on a specific gps unit? Your magnetic heading, corrected via use of the. See answers from pilots and experts on askacfi.com, a forum for flight training questions. Magnetic course is the airplane’s course across the ground, relative to magnetic north. In this article. Bearing is the angle between any two. Is the ground track (trk in garmin) a magnetic or a true course or does it depend on a specific gps unit? We will call course the trajectory to follow, it is the planned or desired. Magnetic course (mc) and magnetic heading (mh) are two essential concepts in navigation, particularly in aviation and. See answers from pilots and experts on askacfi.com, a forum for flight training questions. Intuitively, ground track should be a true course as it is (presumably). Your magnetic heading, corrected via use of the. While they are related, they refer to. Lines of variation are shown on a sectional chart as dashed magenta. Learn the definitions and differences of these three terms related to aircraft orientation and trajectory. There are a lot of different terms that we use when we plan flights: Intuitively, ground track should be a true course as it is (presumably). Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. Learn the differences and roles of true course, true heading, and magnetic heading in aviation navigation. We will call course the trajectory to follow, it is the planned or desired. Find out how to calculate them and why they matter for pilots. Magnetic course is the airplane’s course across the ground, relative to magnetic north. Bearing is the angle between any two. Magnetic course (mc) and magnetic heading (mh) are two essential concepts in navigation, particularly in aviation and maritime contexts. Here is a cheat sheet showing the difference between true course, headings, & bearings along with a list of what is described in magnetic verses true, and statute miles (sm). Your magnetic heading, corrected via use of the. See answers from pilots and experts on askacfi.com, a forum for flight training questions. The reference is the true north, the closest point to the axis of rotation of the planet; The difference between magnetic course (mc) and magnetic heading (mh) lies in their references to direction in navigation. The difference between true north and magnetic north is known as variation.True Course vs True Heading vs (How Are They Different?)
PPT Navigation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5588047
Aviation Heading Chart at Lee Porter blog
Reading A Compass Degrees
Compass Heading vs Heading [True North, North and
The Difference Between True and Heading Airplane Academy
True and Course Courses and Headings in Navigation (Part 1/2
The Difference Between True and Heading Airplane Academy
Enriching an NMEA Stream
Navigation The Effect of Wind Learn To Fly
Is The Ground Track (Trk In Garmin) A Magnetic Or A True Course Or Does It Depend On A Specific Gps Unit?
Lines Of Variation Are Shown On A Sectional Chart As Dashed Magenta.
Magnetic Heading Is Where The Airplane Is Pointed.
The Reference Is The North Of The Earth’s Magnetic.
Related Post: