Crash Course Muscle Contraction
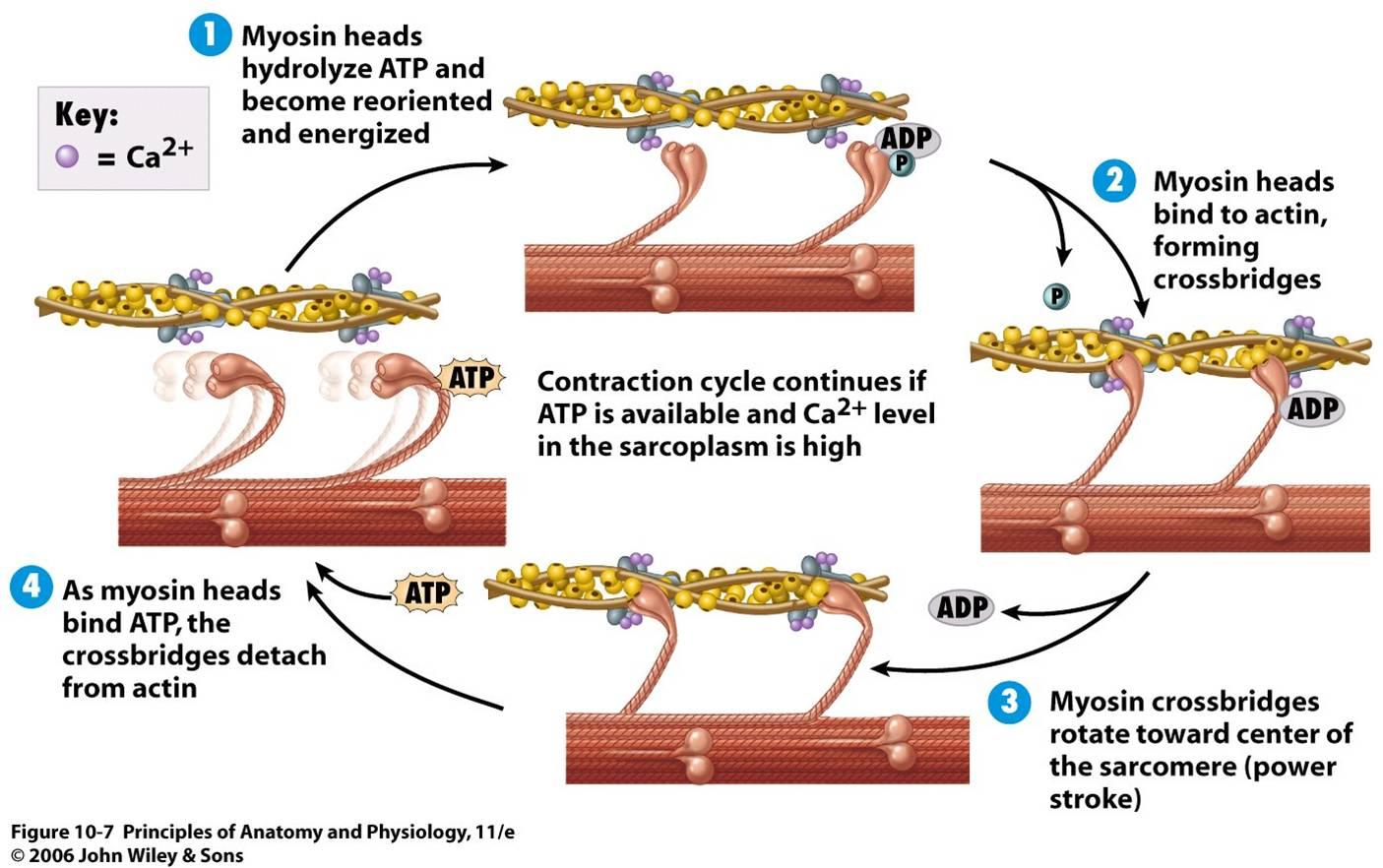
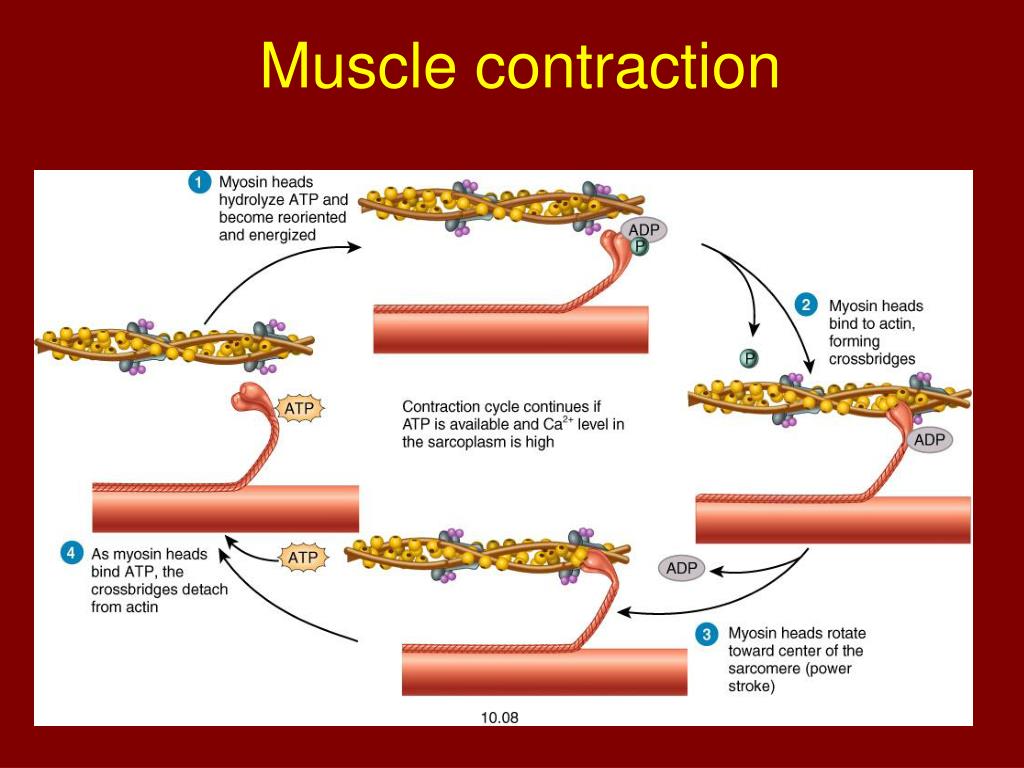
Crash Course Muscle Contraction - Hank and claire also demonstrate the role size plays in motor units, the three phase cycle of muscle twitches, and how the strength and frequency of an impulse affects the strength and duration of a contraction. But how exactly does this happen on the. All of this twitching happens in individual motor units. Contraction of skeletal muscles physiologic anatomy of skeletal muscles mechanism of muscle contraction energetics of muscle contraction whole muscle contrac. The sliding filament model is a widely accepted explanation of how muscle contraction occurs at the molecular level. Prolonged contraction leads to muscle fatigue, and when your muscles just can’t take it anymore all that tension crashes to zero. Your smooth, cardiac, and skelet. Now that we know how muscle contractions happen, let's look at our two main flavors: We're kicking off our exploration of muscles with a look at the complex and important relationship between actin and myosin. Integrate knowledge about how sarcomeres, myofibrils, atp, and calcium ions work together to facilitate muscle contraction and support organism mobility. I can do this workout myself. All of this twitching happens in individual motor units. Prolonged contraction leads to muscle fatigue, and when your muscles just can’t take it anymore all that tension crashes to zero. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and repeat the process. This process is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Your skeletal muscles are constructed like a rope made of bundles of protein fibers, and that the smallest strands are your actin and myosin myofilaments. According to this model, muscle fibers contract when the thin actin filaments slide past the thick myosin filaments within the sarcomeres, the basic units of muscle structure. We're kicking off our exploration of muscles with a look at the complex and important relationship between actin and myosin. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and repeat the process. The pair have some obstacles to overcome. Your skeletal muscles are constructed like a rope made of bundles of protein fibers, and that the smallest strands are your actin and myosin myofilaments. Your smooth, cardiac, and skelet. According to this model, muscle fibers contract when the thin actin filaments slide past the thick myosin filaments within the sarcomeres, the basic units of muscle structure. Your smooth, cardiac,. The pair have some obstacles to overcome. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and repeat the process. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by contracting and releasing in a process called the sliding filament model. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, skeletal muscle and more. This process is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Your skeletal muscles are constructed like a rope made of bundles of protein fibers, and that the smallest strands are your actin and myosin myofilaments. I can do this workout myself. Study. Contraction of skeletal muscles physiologic anatomy of skeletal muscles mechanism of muscle contraction energetics of muscle contraction whole muscle contrac. Hank and claire also demonstrate the role size plays in motor units, the three phase cycle of muscle twitches, and how the strength and frequency of an impulse affects the strength and duration of a contraction. Study with quizlet and. Your smooth, cardiac, and skelet. But how exactly does this happen on the. Integrate knowledge about how sarcomeres, myofibrils, atp, and calcium ions work together to facilitate muscle contraction and support organism mobility. I can do this workout myself. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by contracting and releasing in a process called the sliding filament model. Integrate knowledge about how sarcomeres, myofibrils, atp, and calcium ions work together to facilitate muscle contraction and support organism mobility. This episode also explains twitch summation, tetanus, and isotonic vs. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and. 😑 the process of muscle contraction encapsulates intricate biochemistry, highlighting the importance of calcium ions and atp. This episode also explains twitch summation, tetanus, and isotonic vs. Contraction of skeletal muscles physiologic anatomy of skeletal muscles mechanism of muscle contraction energetics of muscle contraction whole muscle contrac. The pair have some obstacles to overcome. Now that we know how muscle. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by contracting and releasing in a process called the sliding filament model. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by contracting and releasing in a process called the sliding filament model. This process is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. This process is called the sliding filament model of. Now that we know how muscle contractions happen, let's look at our two main flavors: Prolonged contraction leads to muscle fatigue, and when your muscles just can’t take it anymore all that tension crashes to zero. All of this twitching happens in individual motor units. This episode also explains twitch summation, tetanus, and isotonic vs. With its energy spent, the. 😑 the process of muscle contraction encapsulates intricate biochemistry, highlighting the importance of calcium ions and atp. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and repeat the process. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by contracting and releasing in a process called the sliding filament. We've learned about the types of muscle, including skeletal muscle, and we know then when these muscles contract, we are able to move our bodies around. According to this model, muscle fibers contract when the thin actin filaments slide past the thick myosin filaments within the sarcomeres, the basic units of muscle structure. Hank and claire also demonstrate the role size plays in motor units, the three phase cycle of muscle twitches, and how the strength and frequency of an impulse affects the strength and duration of a contraction. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. Your smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles create movement by contracting and releasing in a process called the sliding filament model. A muscle contraction that pulls on the bones and produces movement of body parts This episode also explains twitch summation, tetanus, and isotonic vs. The pair have some obstacles to overcome. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and repeat the process. Integrate knowledge about how sarcomeres, myofibrils, atp, and calcium ions work together to facilitate muscle contraction and support organism mobility. Hank tells us the story of the complicated chemical dance that allows our skeletal muscles to contract and relax. Now that we know how muscle contractions happen, let's look at our two main flavors: This episode also explains twitch summation, tetanus, and isotonic vs. 💪 understanding the three types of muscle tissue—smooth, cardiac, and skeletal—provides insight into how different muscles function in the body. With its energy spent, the myosin releases the ___________ and detaches from the actin, only to bind to another atp and repeat the process. 😑 the process of muscle contraction encapsulates intricate biochemistry, highlighting the importance of calcium ions and atp.PPT Muscular Contractions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Muscle Contraction Presentation
PPT CHAPTER 10 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID724543
Muscle contractionMechanism explained at Molecular level YouTube
Muscle Contraction Cross Bridge Cycle, Animation. Skeletal muscle
muscle contraction Diagram Quizlet
PPT Muscular Contractions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
PPT Crash course Muscular system PowerPoint Presentation, free
Chapter 9 Includes Crash Course Videos part 1 and 2 ppt download
Muscles, Part 2 Organismal Level Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Cardiac Muscle, Smooth Muscle, Skeletal Muscle And More.
Contraction Of Skeletal Muscles Physiologic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscles Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction Energetics Of Muscle Contraction Whole Muscle Contrac.
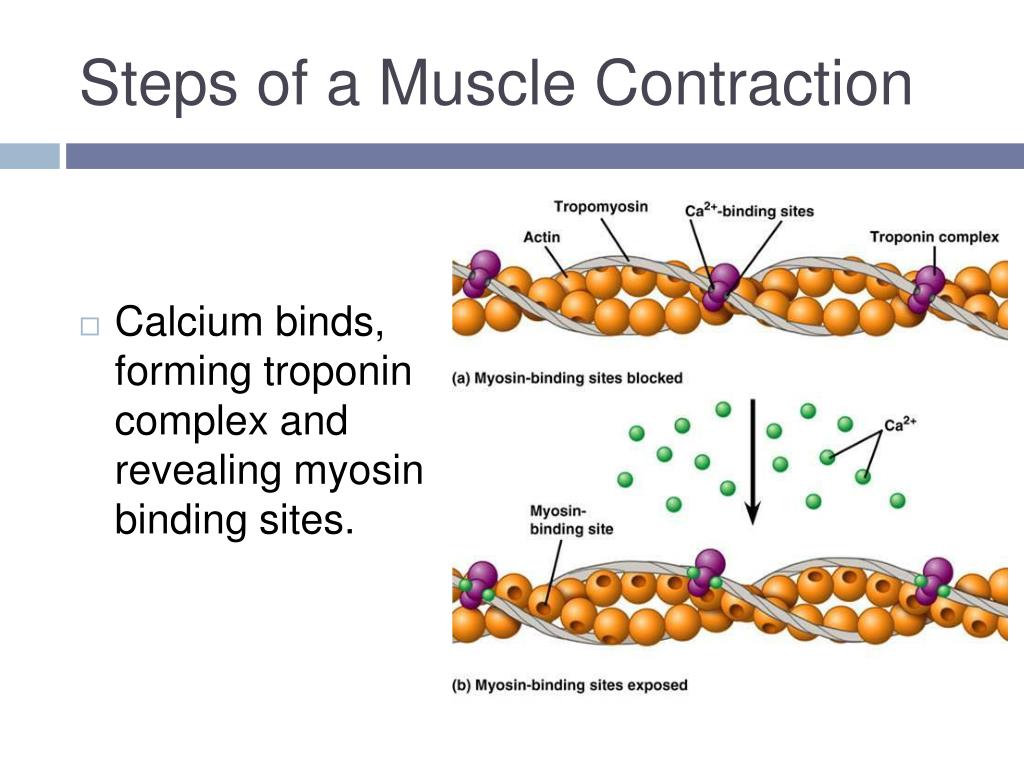
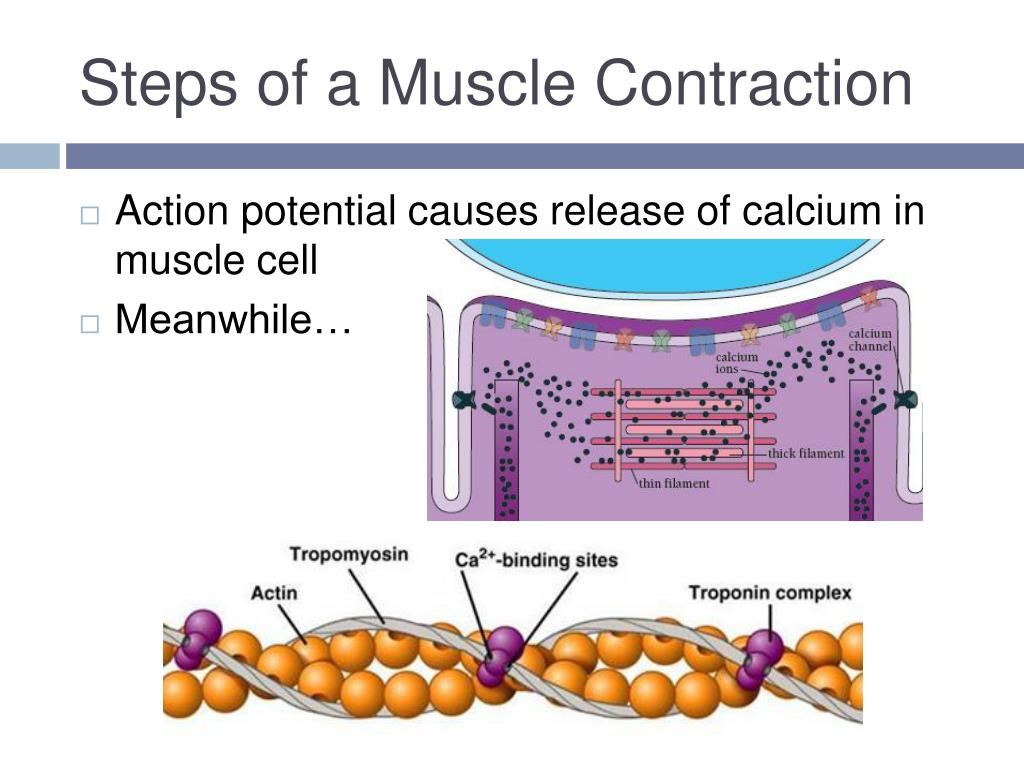
Your Smooth, Cardiac, And Skeletal Muscles Create Movement By Contracting And Releasing In A Process Called The Sliding Filament Model.
All Of This Twitching Happens In Individual Motor Units.
Related Post: