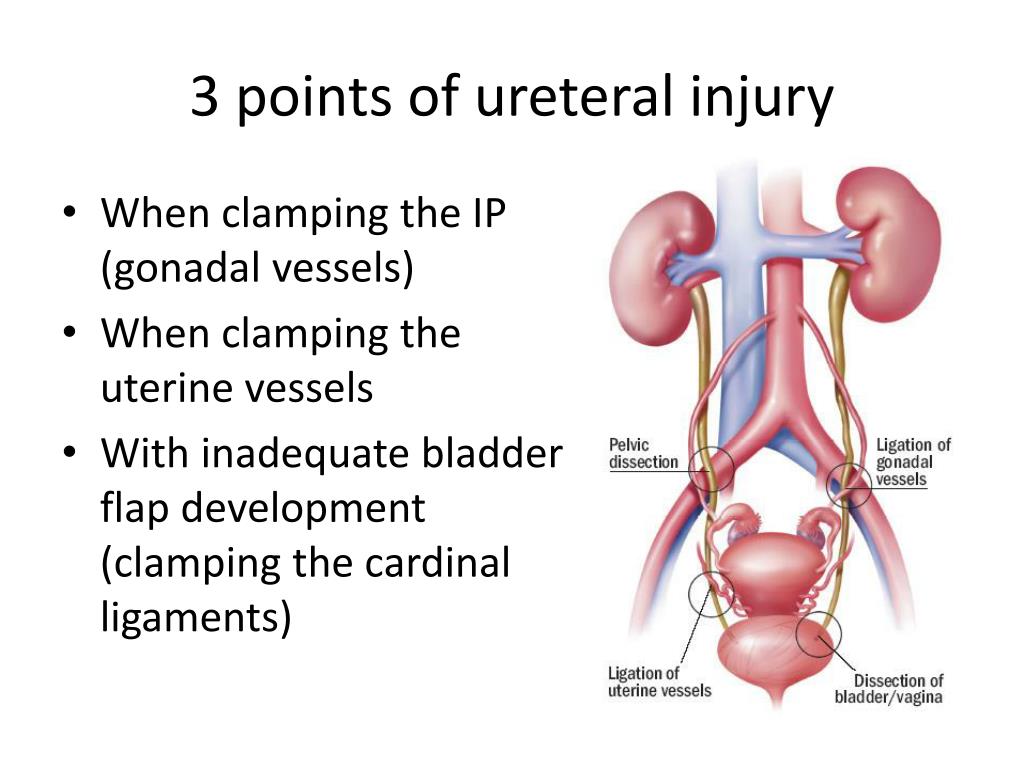
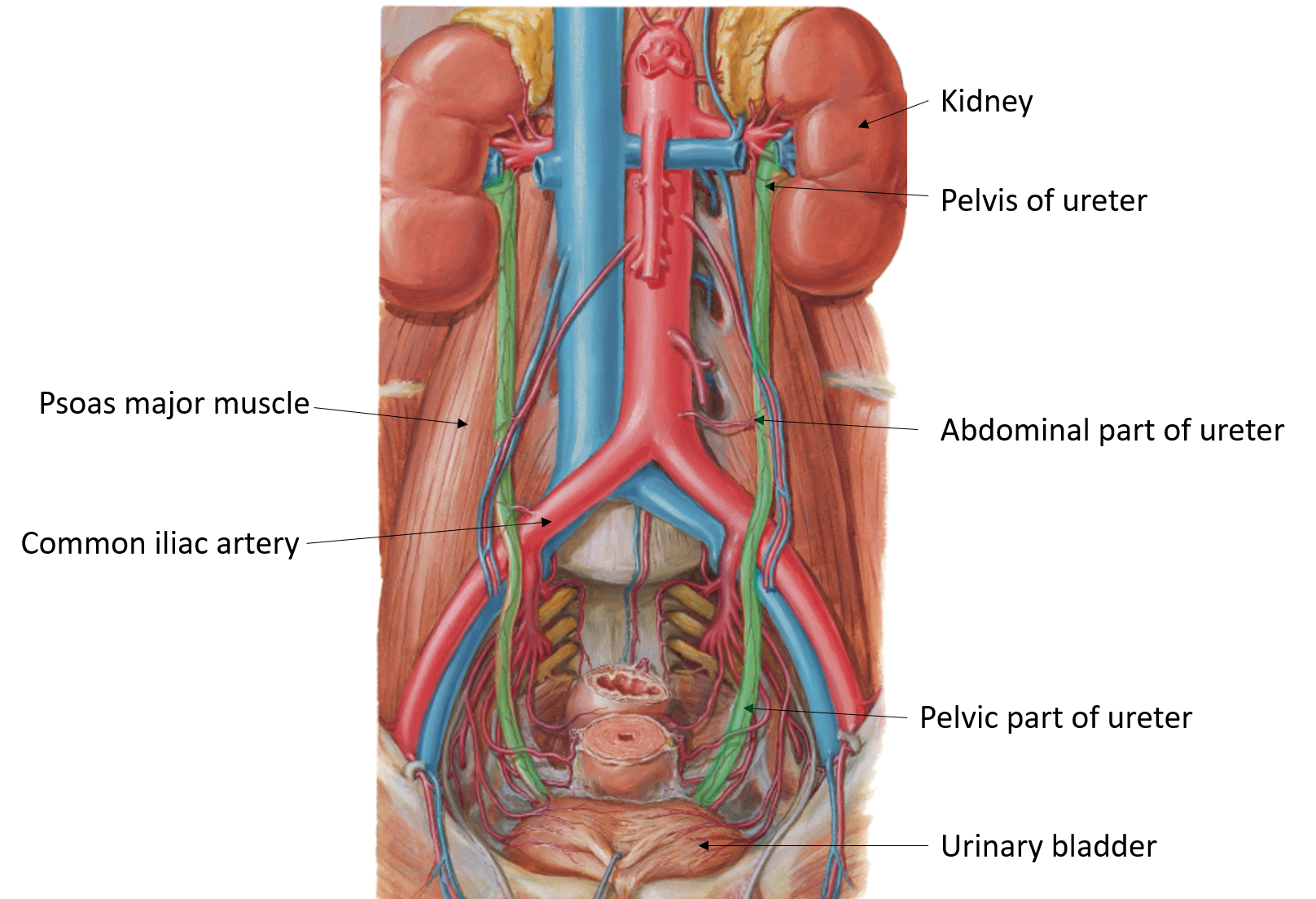
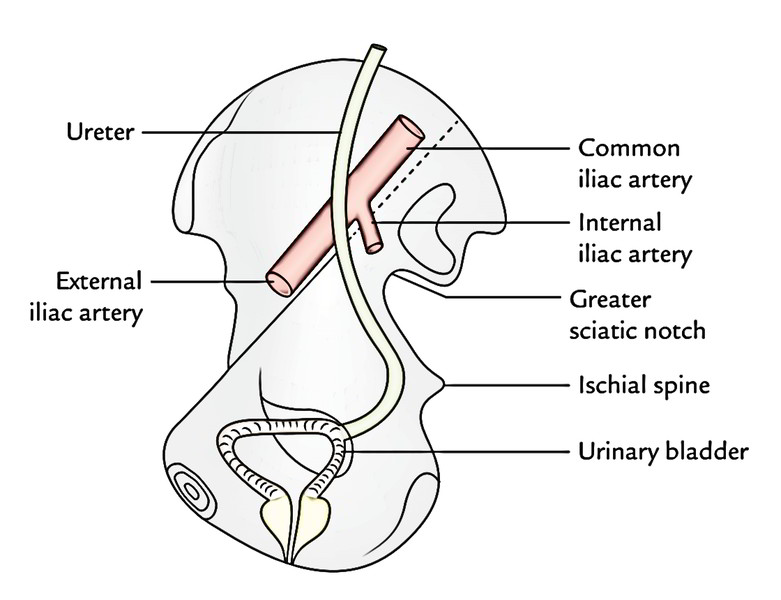
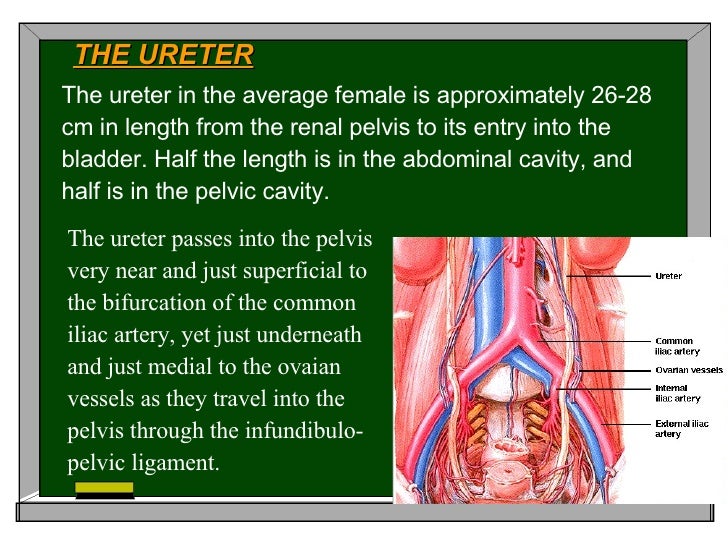
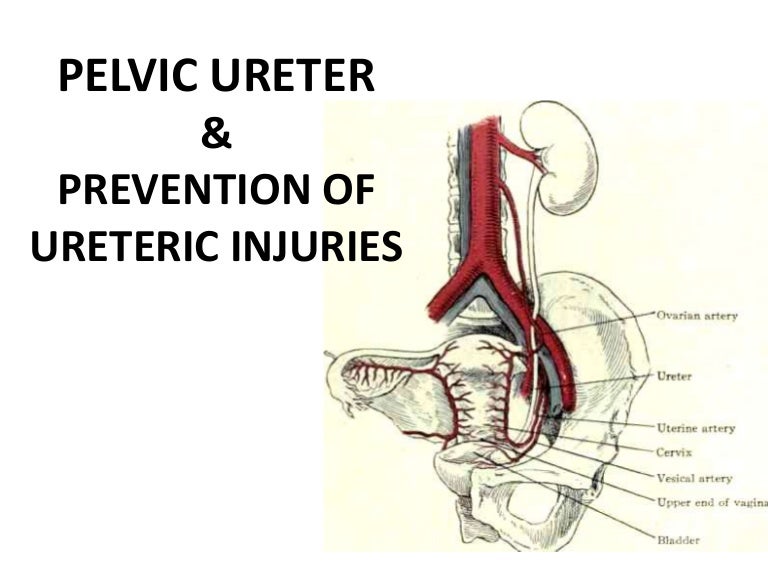
Course Of Ureter In Female Pelvis
Course Of Ureter In Female Pelvis - Thus, if there is any abnormality in. From the pelvic brim to the bladder. The urethra is a fibromuscular tube that conducts urine from the bladder (and semen from the ductus deferens) to the exterior. Turn downward through wall of pelvis3.cross ureteric canal4. On radiographs, the ureter is divided into three sections [fig. Its upper half courses in the abdomen (abdominal part) while its lower half courses in the pelvis (pelvic part). Fast shippingshop best sellersshop our huge selectiondeals of the day Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine artery crosses the ureter. In the pelvis, they receive additional branches from the internal. However, they do not work like other body sphincters, preventing reflux. In general the ureter is seen crossing the external iliac vessels from lateral to. Within the abdomen, the ureters descend retroperitoneally and anterior to the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall (psoas major), eventually, they reach the pelvic brim where they. The urethra is a fibromuscular tube that conducts urine from the bladder (and semen from the ductus deferens) to the exterior. In females, they sit posterior to the ovary, and then run adjacent to the cervix and lateral fornices of the vagina before entering the bladder. In the female, the ureter forms, as it lies in relation to the wall of the pelvis, the posterior boundary of a shallow depression named the ovarian fossa, in which the ovary is situated. Radiographic anatomy of the ureter]:. In females, the ureters pass medial to the origin of the uterine artery. Cross pelvic brim infront of internal iliac artery bifurcation2. Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine artery crosses the ureter. Finally, the ureters pass through the bladder wall in. In the pelvis, they receive additional branches from the internal. Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine artery crosses the ureter. In general the ureter is seen crossing the external iliac vessels from lateral to. From the renal pelvis to the pelvic brim. It begins at the neck of the bladder, traverses the pelvic and. In females, they sit posterior to the ovary, and then run adjacent to the cervix and lateral fornices of the vagina before entering the bladder. Finally, the ureters run near the lateral part. In the pelvis, they receive additional branches from the internal. From the pelvic brim to the bladder. Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine. In the female, the ureter forms, as it lies in relation to the wall of the pelvis, the posterior boundary of a shallow depression named the ovarian fossa, in which the ovary is situated. However, they do not work like other body sphincters, preventing reflux. Cross pelvic brim infront of internal iliac artery bifurcation2. Finally, the ureters pass through the. Cross pelvic brim infront of internal iliac artery bifurcation2. In the pelvis, they receive additional branches from the internal. Within the abdomen, the ureters descend retroperitoneally and anterior to the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall (psoas major), eventually, they reach the pelvic brim where they. Finally, the ureters run near the lateral part. In females, they sit posterior to. Its upper half courses in the abdomen (abdominal part) while its lower half courses in the pelvis (pelvic part). Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine artery crosses the ureter. In the female, the ureter forms, as it lies in relation to the wall of the pelvis, the posterior boundary of a shallow depression named the ovarian. In general the ureter is seen crossing the external iliac vessels from lateral to. In the majority of the patients, the course of the ureter is easily demarcated from the level of the pelvic brim. Turn downward through wall of pelvis3.cross ureteric canal4. In females, the ureters pass medial to the origin of the uterine artery. From the renal pelvis. From the renal pelvis to the pelvic brim. Finally, the ureters pass through the bladder wall in. The ureters regulate the course of the urine, in a single direction. In females, the ureters pass medial to the origin of the uterine artery. In the majority of the patients, the course of the ureter is easily demarcated from the level of. Within the abdomen, the ureters descend retroperitoneally and anterior to the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall (psoas major), eventually, they reach the pelvic brim where they. Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine artery crosses the ureter. From the pelvic brim to the bladder. However, they do not work like other body sphincters, preventing reflux. In. However, they do not work like other body sphincters, preventing reflux. Finally, the ureters pass through the bladder wall in. In the majority of the patients, the course of the ureter is easily demarcated from the level of the pelvic brim. On radiographs, the ureter is divided into three sections [fig. From the pelvic brim to the bladder. Its upper half courses in the abdomen (abdominal part) while its lower half courses in the pelvis (pelvic part). In the pelvis, they receive additional branches from the internal. In the majority of the patients, the course of the ureter is easily demarcated from the level of the pelvic brim. Turn downward through wall of pelvis3.cross ureteric canal4. From the. In the female, the ureter forms, as it lies in relation to the wall of the pelvis, the posterior boundary of a shallow depression named the ovarian fossa, in which the ovary is situated. During their course in the abdomen, the ureters receive blood from the gonadal vessels, aorta, and retroperitoneal vessels. On radiographs, the ureter is divided into three sections [fig. From the pelvic brim to the bladder. In females, they sit posterior to the ovary, and then run adjacent to the cervix and lateral fornices of the vagina before entering the bladder. Finally, the ureters run near the lateral part. So, the ureter has two divisions: Finally, the ureters pass through the bladder wall in. Fast shippingshop best sellersshop our huge selectiondeals of the day Turn downward through wall of pelvis3.cross ureteric canal4. It begins at the neck of the bladder, traverses the pelvic and. In the pelvis, they receive additional branches from the internal. Then, at the level of the ischial spine, the uterine artery crosses the ureter. In the majority of the patients, the course of the ureter is easily demarcated from the level of the pelvic brim. From the renal pelvis to the pelvic brim. In general the ureter is seen crossing the external iliac vessels from lateral to.Female Pelvic Anatomy Ureter ANATOMY STRUCTURE
Anatomy of the Female Urinary Tract Obgyn Key
PPT Pelvic Surgical Anatomy PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Ureter Anatomy QA
Cardinal Ligament Ureter
Course of pelvic ureters. Taken from [1]. Download Scientific Diagram
Ureter Earth's Lab
Anatomy2009
Pelvic ureter
Course of ureter female Diagram Quizlet
However, They Do Not Work Like Other Body Sphincters, Preventing Reflux.
In The Female, The Ureter Forms, As It Lies In Relation To The Wall Of The Pelvis, The Posterior Boundary Of A Shallow Depression Named The Ovarian Fossa, In Which The Ovary Is Situated.
Its Upper Half Courses In The Abdomen (Abdominal Part) While Its Lower Half Courses In The Pelvis (Pelvic Part).
The Ureters Regulate The Course Of The Urine, In A Single Direction.
Related Post: