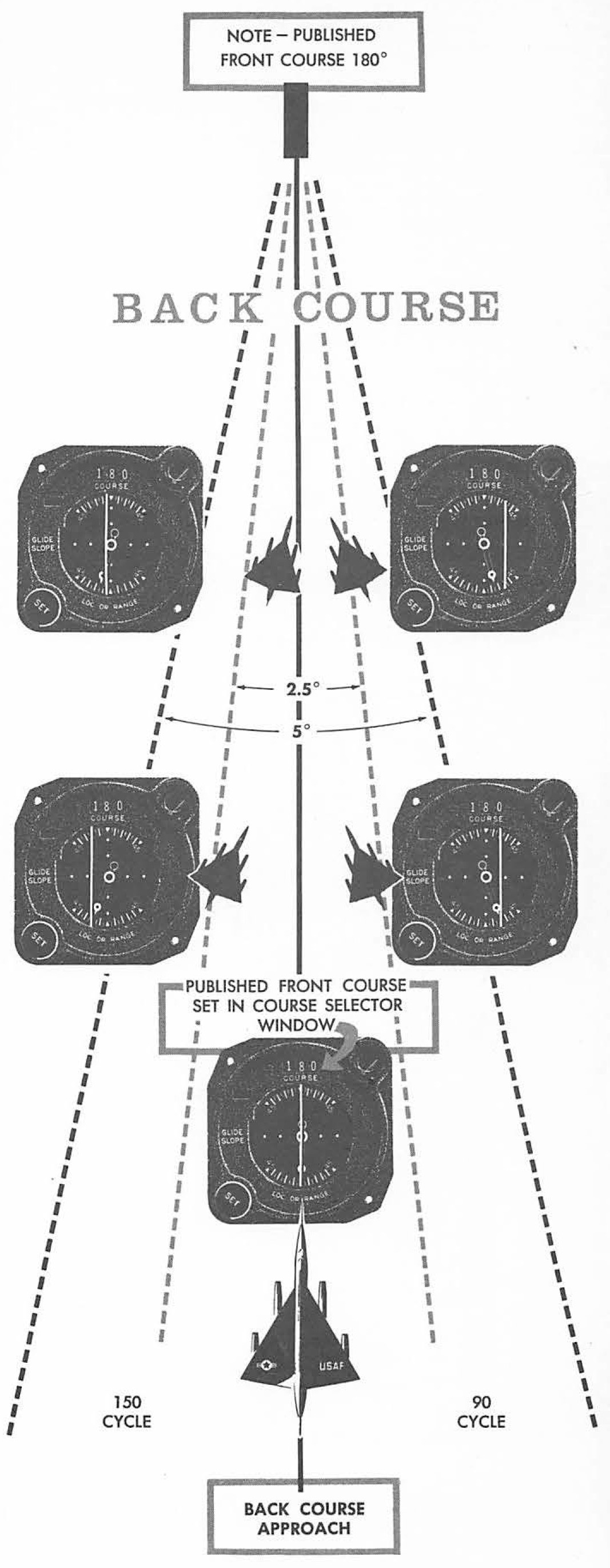
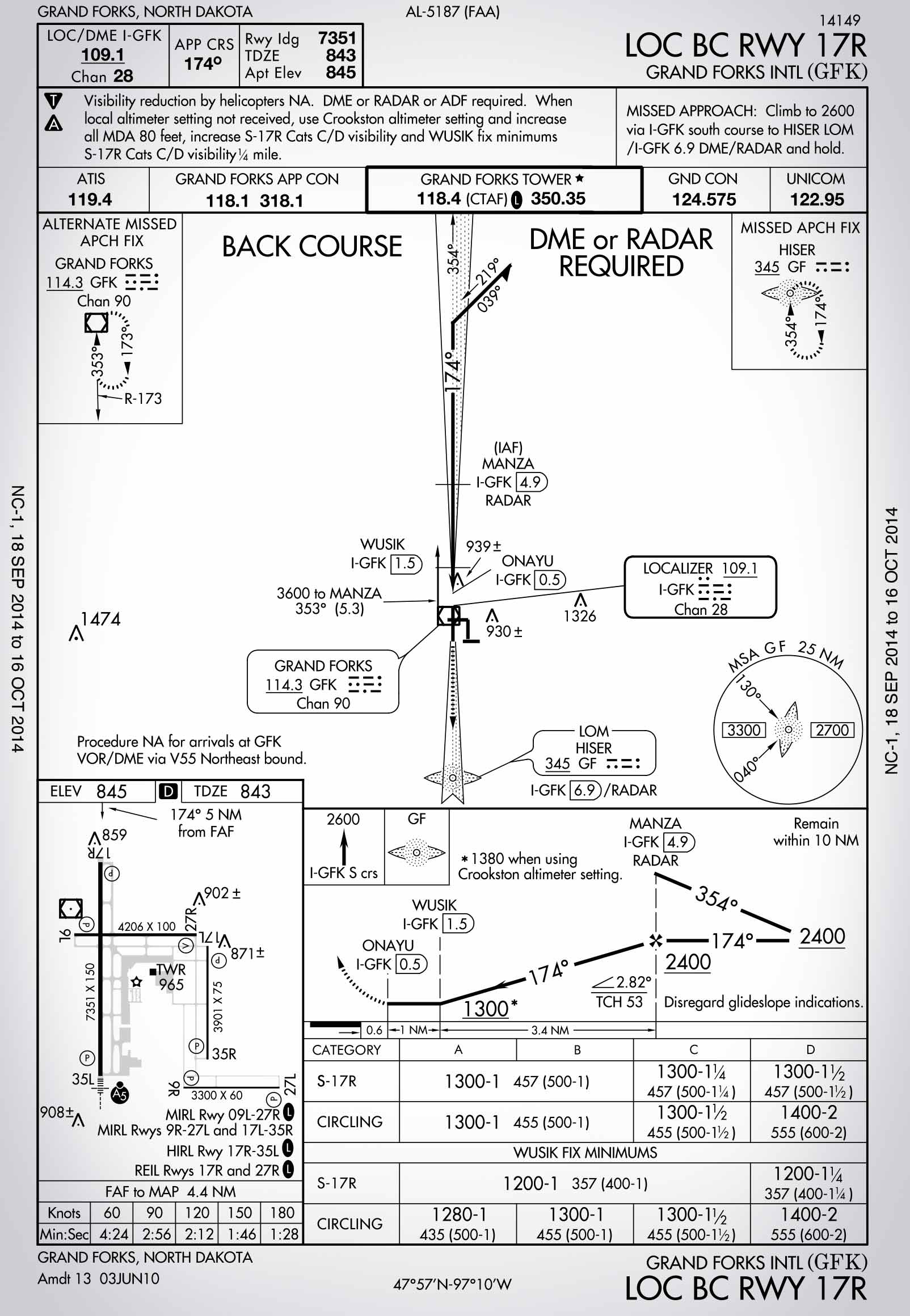
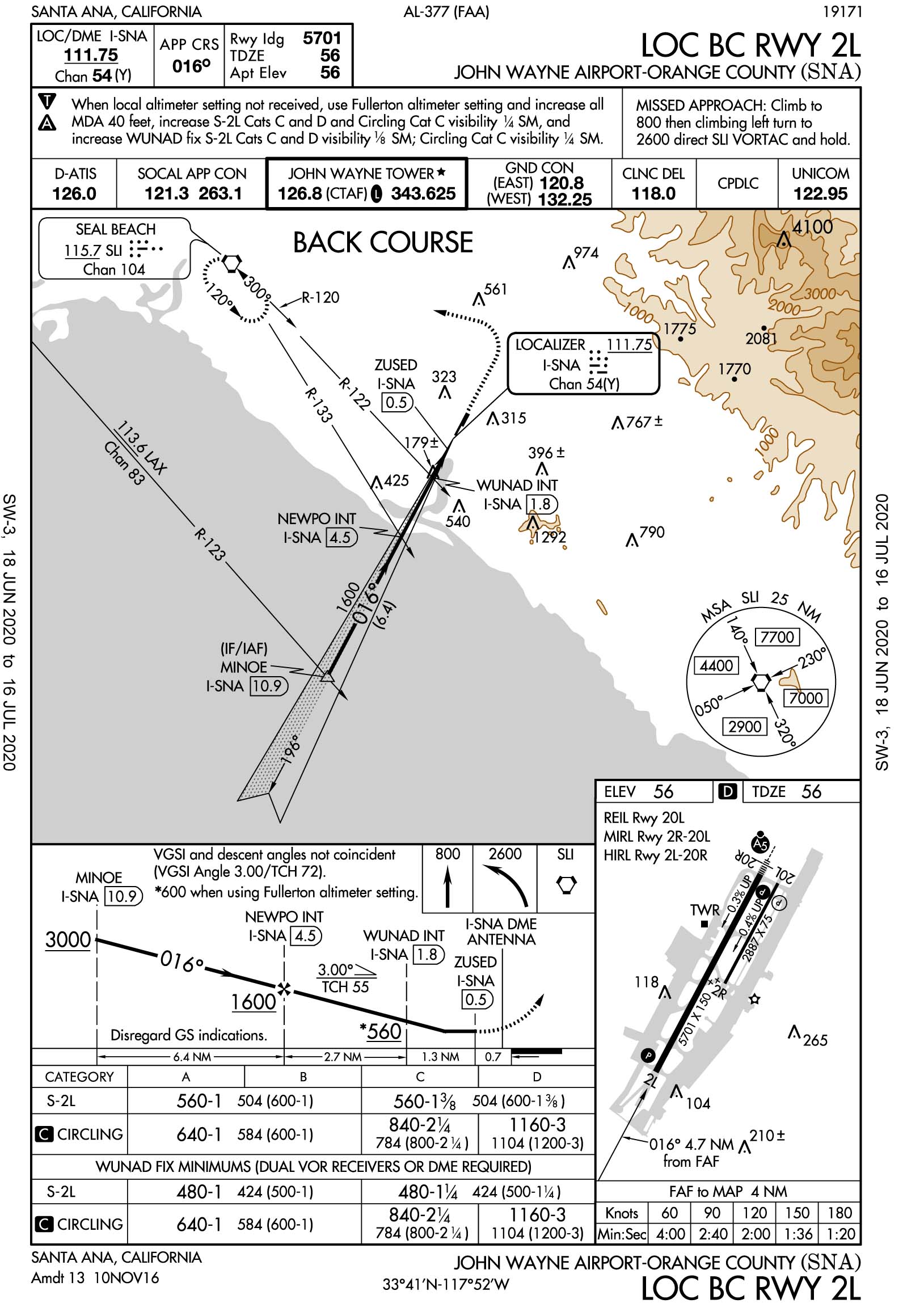
Back Course Localizer
Back Course Localizer - A localizer (loc) (above left) transmits vhf signals (108.1 mhz to 111.95 mhz) to provide aircraft with lateral guidance that allows pilots to ensure their aircraft is properly. A localizer sends out a signal in two directions, the one opposite to the approach to the runway is the back course, and it can also be used for lateral navigation, though the. The third reminder is the back course. In aviation, a localizer is the lateral component of the instrument landing system (ils) for the runway centerline when combined with the vertical glide path, not to be confused with a locator, although both are parts of aviation navigation systems. Your hsi course points back to the runway and you’ve got a right needle deflection. The two primary differences between a. Master your navigational skills using a map and compass. The localizer back course provides several opportunities to make mistakes setting the back course instead of the front course or forgetting to press the flight director's bc. The shaded half of the feather is on the left side of the inbound course, indicating it’s the “back” of the localizer signal for runway 2. This video reviews a localizer back course approach plate and how to fly a localizer back course approach using flight simulation and hsi/cdi training software. At certain locations with ils or localizer approaches, the back course of the localizer is utilized in a published iap to serve the reciprocal runway. Learn what a back course approach is, how to set up and fly it with a cdi or hsi, and where you'll find it. The shaded half of the feather is on the left side of the inbound course, indicating it’s the “back” of the localizer signal for runway 2. The two primary differences between a. A localizer (like a glide path) requires both a transmitting airport runway system and receiving cockpit instruments. Master your navigational skills using a map and compass. This video reviews a localizer back course approach plate and how to fly a localizer back course approach using flight simulation and hsi/cdi training software. A localizer sends out a signal in two directions, the one opposite to the approach to the runway is the back course, and it can also be used for lateral navigation, though the. The third reminder is the back course. While not as common as. A localizer back course has a lot higher chance of interference, since between the plane on approach and the antenna is usually a fence, a road, trees, etc. A localizer sends out a signal in two directions, the one opposite to the approach to the runway is the back course, and it can also be used for lateral navigation, though. The localizer back course provides several opportunities to make mistakes setting the back course instead of the front course or forgetting to press the flight director's bc. You’re outbound on the localizer back course. This video reviews a localizer back course approach plate and how to fly a localizer back course approach using flight simulation and hsi/cdi training software. A. Orient your map so it matches what you see around you while exploring nature in the heritage quarries. At certain locations with ils or localizer approaches, the back course of the localizer is utilized in a published iap to serve the reciprocal runway. Master your navigational skills using a map and compass. The third reminder is the back course. Learn. The localizer back course provides several opportunities to make mistakes setting the back course instead of the front course or forgetting to press the flight director's bc. A localizer back course has a lot higher chance of interference, since between the plane on approach and the antenna is usually a fence, a road, trees, etc. The third reminder is the. The shaded half of the feather is on the left side of the inbound course, indicating it’s the “back” of the localizer signal for runway 2. The localizer back course provides several opportunities to make mistakes setting the back course instead of the front course or forgetting to press the flight director's bc. At certain locations with ils or localizer. First, every instrument landing system (ils) or localizer (loc) approach generates a back course as part of the radio signal that makes up the front courses of these approaches. A localizer back course has a lot higher chance of interference, since between the plane on approach and the antenna is usually a fence, a road, trees, etc. A localizer (loc). A localizer (like a glide path) requires both a transmitting airport runway system and receiving cockpit instruments. In aviation, a localizer is the lateral component of the instrument landing system (ils) for the runway centerline when combined with the vertical glide path, not to be confused with a locator, although both are parts of aviation navigation systems. An older aircraft. A localizer sends out a signal in two directions, the one opposite to the approach to the runway is the back course, and it can also be used for lateral navigation, though the. This video reviews a localizer back course approach plate and how to fly a localizer back course approach using flight simulation and hsi/cdi training software. While not. In aviation, a localizer is the lateral component of the instrument landing system (ils) for the runway centerline when combined with the vertical glide path, not to be confused with a locator, although both are parts of aviation navigation systems. A localizer (like a glide path) requires both a transmitting airport runway system and receiving cockpit instruments. The two primary. A localizer (loc) (above left) transmits vhf signals (108.1 mhz to 111.95 mhz) to provide aircraft with lateral guidance that allows pilots to ensure their aircraft is properly. You’re outbound on the localizer back course. The shaded half of the feather is on the left side of the inbound course, indicating it’s the “back” of the localizer signal for runway. The third reminder is the back course. While not as common as. The two primary differences between a. The course explorer provides the schedule of classes by term and a browsable database of general education requirements in addition to other resources. First, every instrument landing system (ils) or localizer (loc) approach generates a back course as part of the radio signal that makes up the front courses of these approaches. At certain locations with ils or localizer approaches, the back course of the localizer is utilized in a published iap to serve the reciprocal runway. This video reviews a localizer back course approach plate and how to fly a localizer back course approach using flight simulation and hsi/cdi training software. Learn what a back course approach is, how to set up and fly it with a cdi or hsi, and where you'll find it. A localizer (loc) (above left) transmits vhf signals (108.1 mhz to 111.95 mhz) to provide aircraft with lateral guidance that allows pilots to ensure their aircraft is properly. The localizer back course provides several opportunities to make mistakes setting the back course instead of the front course or forgetting to press the flight director's bc. A localizer (like a glide path) requires both a transmitting airport runway system and receiving cockpit instruments. A localizer sends out a signal in two directions, the one opposite to the approach to the runway is the back course, and it can also be used for lateral navigation, though the. A localizer back course has a lot higher chance of interference, since between the plane on approach and the antenna is usually a fence, a road, trees, etc. You’re outbound on the localizer back course. The shaded half of the feather is on the left side of the inbound course, indicating it’s the “back” of the localizer signal for runway 2. An older aircraft without an ils receiver cannot take advantage of any ils f…How To Fly A Localizer Back Course Approach Boldmethod Courses
Localizer Back Course ( LOC BC ) Tutorial with NAVIGRAPH YouTube
Back Course Localizer
Could You Fly This Localizer Back Course Approach? Boldmethod
How To Fly A Localizer Back Course Approach Boldmethod
Making Sense of the BackCourse Approach How to prepare before you
How to Fly a Localizer Back Course Approach Localizer Back Course
How To Fly A Localizer Back Course Approach Aviation education
How To Fly A Localizer Back Course Approach By Swayne Martin 03/24
LOCALIZER BACK COURSE
Master Your Navigational Skills Using A Map And Compass.
A Back Course Approach Uses The Opposite Side Of A Localizer Antenna From A Standard Approach, And Requires Reverse Sensing Or Normal Sensing Depending On The Instrument.
Your Hsi Course Points Back To The Runway And You’ve Got A Right Needle Deflection.
Orient Your Map So It Matches What You See Around You While Exploring Nature In The Heritage Quarries.
Related Post: